A team of engineers in Korea has developed a microrobot based on magnetically powered human nuclear transfer stem cells (hNTSC). It can be used for minimally invasive targeted stem cell delivery to the brain through the intranasal pathway. The stem cell-based microrobot bypasses the blood-brain barrier, which is a unique and specific component of the cerebrovascular network.
The team developed the robot by internalizing iron oxide nanoparticles with high biocompatibility and superparamagnetism into stem cells extracted from human nasal turbinate. The magnetically powered hNTSC-based microrobot can be freely and reliably be manipulated within the human body using an externally-controlled rotating magnetic field. It can be remotely controlled within the microfluidic channel, facilitating quick and accurate delivery to the target point.
Using an ex vivo model based on brain organoids, researchers further determined that the newly developed “Cellbots” can be reliably transplanted into brain tissue. Using a murine model, it is finally demonstrated that the Cellbots can be intranasally administered and magnetically guided to the target tissue in vivo for precise delivery to the cerebral cortex, accomplishing a successful transplant. This approach has the potential to effectively treat central nervous system disorders in a minimally invasive manner.
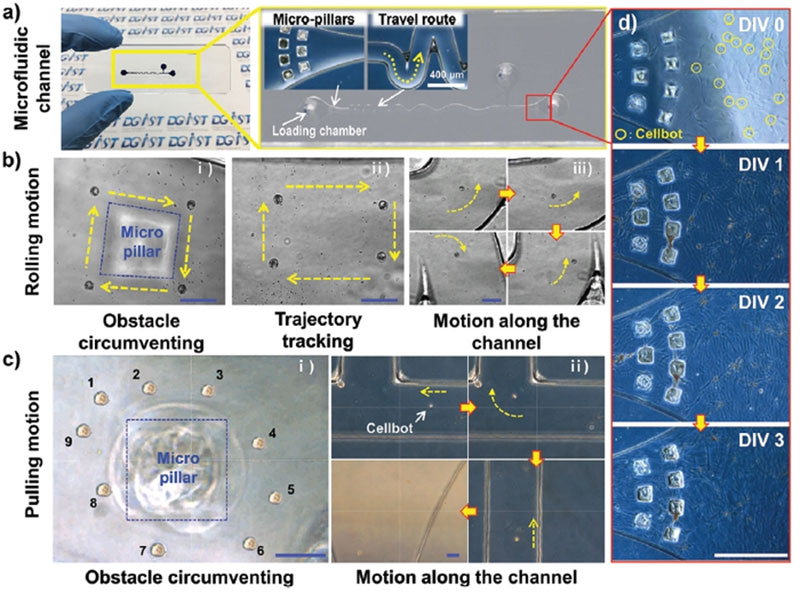
The new technology is superior in efficacy and safety compared to the conventional surgical method. It is expected to bring new possibilities of treating various intractable neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and brain tumors in the future.
“This research overcomes the limitations in the delivery of a therapeutic agent into brain tissues owing to the blood-brain barrier,” said Prof. Hongsoo Choi (DGIST). “It opens new possibilities for the treatment of various intractable neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and brain tumors, by enabling accurate and safe targeted delivery of stem cells through the movement of a magnetically powered hNTSC-based microrobot via the intranasal pathway.”