The development of the electric transport industry stimulates the search for new solutions in the field of creating rechargeable batteries, which are subject to special requirements in terms of energy consumption, weight, dimensions, and safety. Every year, these requirements are increasing, which leads to the introduction of new manufacturing technologies. An important part of such a battery is the cooling system.
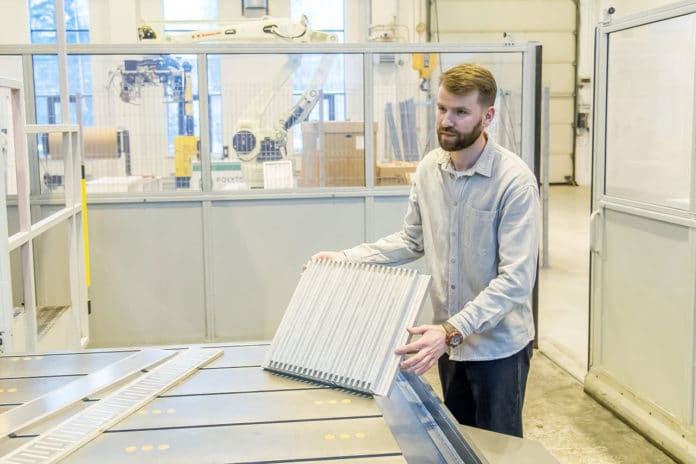
Now, a team of engineers from Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU) has created a compact radiator for lithium-ion batteries, which in the future can be used for electric vehicles. The new radiator is compact, lightweight, and at the same time, durable.
To create such a radiator, engineers used aluminum alloys and also applied friction stir welding technology.
As the engineer of the Laboratory of Light Materials and Structures of SPbPU, Fedor Isupov explained, aluminum alloys were chosen as the basis for the radiator due to their lightness and strength. However, creating an aluminum cooling system using conventional methods, he said, would lead to non-compliance with the requirements – in particular, in terms of dimensions.
“We can’t achieve the required compactness using the traditional methods,” the scientist noted. “The welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys, which is used to create the radiator, is quite complicated. The seam at the junction of the sheets will be very fragile. Friction stir welding helps to avoid the defects inherent in fusion welding. It also speeds up and reduces the cost of the process. Also, thus it possible to obtain solid overlap joints, which are better than the one made by conventional welding.”
It is noted that the obtained radiator is used not only for cooling the battery but also plays the role of the battery bottom. In addition, at low temperatures conditions, heat is supplied through it to heat the batteries. For this, a special control system has been developed.
Engineers have already developed the first sample of the radiator, and soon, they plan to test this cooling system.
