Self-driving car technology is still a long way from being widespread. People are still skeptical that a technology as novel as a self-driving car can be guaranteed to be safe on public roads.
Now, a research team at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology has developed a material that heals scratches on the sensor of an autonomous vehicle. The self-healing lens material can prevent can accidents that occur due to signal distortion by restoring scratches on the sensor surface of the self-driving car.
In many everyday optical devices such as cameras, cell phones, and glasses, a lens is a tool that collects or disperses light. However, if the lens surface is damaged by a scratch, the image or optical signal received by the optical device can be severely distorted.
Traffic accidents caused by recognition errors and malfunctions of vision systems such as LiDAR sensors and image sensors of self-driving cars have repeatedly occurred. As a result, confidence in the safety of self-driving cars is rather low, according to a survey by the American Automobile Association in 2023.
The research team developed a transparent lens material that can remove scratches on the sensor surface within 60 seconds when focused sunlight is irradiated using a simple tool such as a magnifying glass.
Flexible materials are generally advantageous in securing excellent self-healing performance. However, lenses or protecting coating materials are made of hard materials, and thus it is very difficult to impart a self-healing function. As a solution, researchers combined a thiourethane structure, which is already being used as a lens material, and a transparent photothermal dye to design a ‘dynamic chemical bond’ in which the polymers repeat disassembly and recombination under irradiation of sunlight.
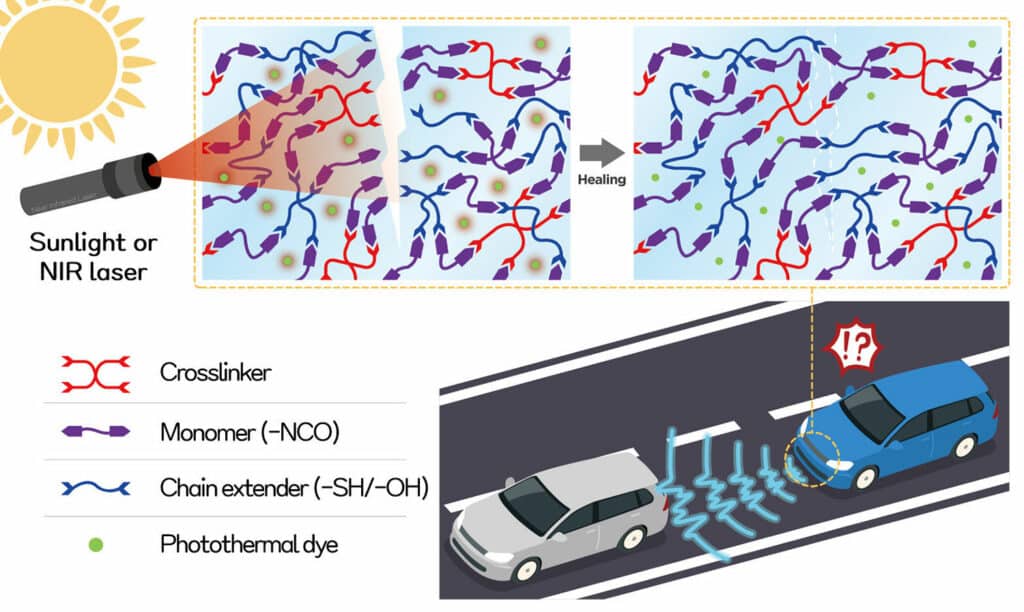
The developed transparent organic photothermal dye can selectively absorb light of a specific near-infrared wavelength (850-1050 nm) without interfering with the visible light region (350-850 nm) used for image sensors and the near-infrared region (about 1550 nm) used for LiDAR sensors.
When photothermal dyes absorb sunlight, the surface temperature of the developed lens material rises as the light energy is converted into thermal energy. The increased surface temperature makes it possible to self-heal a surface scratch by repeating the dissociation and recombination of chemical bonds in the polythiourethane structure.
Researchers claim the developed lens material showed perfect self-healing even when scratches cross each other and provide excellent resilience, maintaining 100% of self-healing efficiency even if the process of scratching and healing at the same location is repeated more than five times.
“This technology is a platform technology that synthesizes self-healing lens materials using both an inexpensive high-refractive polymer material and a photothermal dye. It is expected to be widely used in various applications such as autonomous vehicle sensors as well as glasses and cameras,” said Dr. Lee Young Kuk, president of KRICT.
Journal reference:
- Ji-Eun Jeong, Jae-Won Lee, Mi Ju Bae, Hyoung Eun Bae, Eunjeong Seo, Seulchan Lee, JungYeop Shin, Sang-Ho Lee, Yu Jin Jung, Hyocheol Jung, Young Il Park, In Woo Cheong, Hak-Rin Kim, and Jin Chul Kim. NIR-Triggered High-Efficiency Self-Healable Protective Optical Coating for Vision Systems. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023; DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c21058
